The structure of the “antenna” that a blue-green alga uses to harvest light has been determined by RIKEN researchers and compared with those of four other species. In addition to providing clues about the evolution and diversity of cyanobacteria, this research could inform the development of efficient photoreactive compounds.
The research is published in Nature Communications.
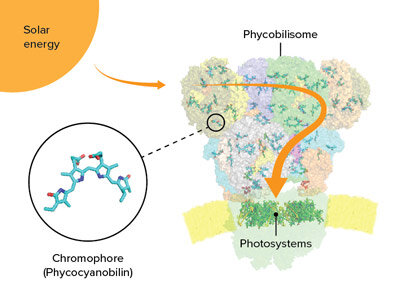
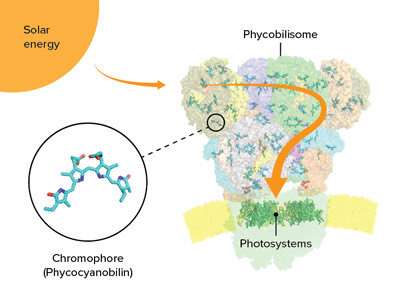
Located on the surface membranes of cyanobacteria (or blue-green algae) and other algae, phycobilisomes are bundles of proteins and chromophores that act as antennas for capturing light during photosynthesis.
“Phycobilisomes absorb light at wavelengths that are difficult for other light-absorbing photosynthetic proteins, such as photosystems I and II, to utilize,” explains Keisuke Kawakami at the RIKEN SPring-8 Center. “Each algal species has its own unique phycobilisome structure. Gaining insights into these structures will boost our knowledge of efficient energy production from sunlight.”
Phycobilisomes come in five shapes, of which the cyanobacterium called Thermosynechococcus vulcanus has the most common one—a half-sphere with a fan-like arrangement of rods protruding from the core. Light energy is absorbed and then transferred through the rods and cores to photosystems I and II.
Now, by using cryo-electron microscopy, Koji Yonekura, also at the RIKEN SPring-8 Center, and his team have analyzed the structure and function of the phycobilisome of T. vulcanus, and compared it with those of four previously reported species.
The researchers discovered that the core consists of five cylinders of proteins, rather than the more common three-cylinder structure, and they also identified a new type of cylinder. Each phycobilisome has several rods projecting from the core, formed of stacked proteins and chromophores connected by linker proteins. T. vulcanus only has one type of chromophore, called phycocyanobilin, whereas some algae have more than one.
“Uncovering the structure of linker proteins and amino acids around each phycocyanobilin, and the interactions between them, is critical for understanding unidirectional energy transfer,” says Kawakami. “We were surprised to find that amino-acid residues located around certain phycocyanobilins can manipulate the absorption wavelengths of those chromophores, enabling continuous and rapid energy transfer even under changing light conditions.”
The team also found that these amino-acid residues differ subtly between algal species, probably as a result of the different light conditions in different growth environments.
“Investigating the phycobilisome structures in different species will help us understand the diversity and evolution of algae,” says Kawakami. “Taking inspiration from phycobilisomes could inform the development of optical devices that exploit the mechanism of unidirectional energy transfer using a single chromophore.”